Oral cancer is cancer that develops anyplace in the mouth or its surrounding area. Signs and symptoms of oral cancer may not always be evident. This kind of cancer can occur even in places you might not have considered, like:
- Inside of cheeks
- Lips
- Gums
- Roof of the mouth
- Tongue
- Under the tongue
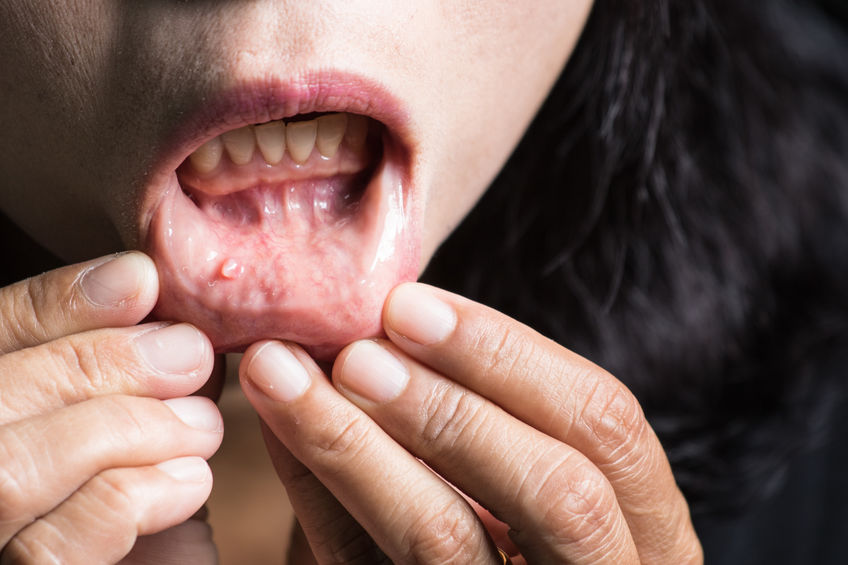
Oral cancer usually begins with the appearance of a whitish patch, similar to a canker sore or blister, which is called leukoplakia. This may be a deep fissure of the affected tissue and may get darker as it progresses. It usually isn’t painful at first, but as it spreads, it will become sore.
Although most often it affects the tongue or lips, oral cancer can also occur in any part of the oral cavity (palate, gums, bottom of the mouth, or cheeks). In most cases, these are squamous cell carcinomas, and they spread rapidly. It is more common in women than in men and usually appears after 40 years of age.
Risk Factors
The main risk factors related to oral cancer are:
- Smoking
- Alcohol consumption
- Chronic papillomavirus (HPV) infection
- Poor dental hygiene
- Chronic irritation caused by an unidentified disease
Symptoms of Oral Cancer
The signs that could indicate oral cancer are:
- Having a sore on the lip or in the mouth that does not heal
- Finding a bulge in the lip or in the mouth or throat
- Seeing a white or red spot on the gums, or tongue
- Having unusual bleeding, pain, or insensitivity in the mouth
- Dealing with a sore throat that does not go away
- Feeling that something is constantly stuck in your throat
- Having difficulty or pain when chewing or swallowing
- Dealing with inflammation of the jaw that does not allow proper placement of dentures
- Hearing a change in your voice
- Having an earache
- Weight loss with no apparent cause
Treatment of Oral Cancer
When the diagnosis occurs in an initial phase, and the tumor is tiny and localized, the treatment of oral cancer involves its surgical removal. Surgery can also be a treatment option in larger tumors, as long as there is no lymph node involvement, and should be complemented with chemotherapy and radiotherapy. In these cases, the cure rate can reach up to 90%.
Oral Cancer Screening
The oral cancer screening performed by a dentist is not painful and only takes a few minutes. It can be done during the routine dental examination.
This is what you should expect:
- You will be asked to remove any dentures or partial dentures you have.
- Our friendly experts will examine your face, neck, lips, and mouth to look for visible signs of oral cancer.
- The dentist will palpate the area under the jaw and the sides of the neck with both hands to detect lumps.
- The dentist will check the inside of your lips and cheeks.
- You will be asked to stick your tongue out to check for inflammation, discoloration, or abnormal texture.
- Then the dentist will gently move your tongue from one side to the other to detect signs of cancer under the tongue or at its base.
- Finally, the dentist will check your throat, as well as your palate and the base of your mouth.
You should have an oral cancer screening once a year. To get your mouth checked out, call us today at 317-745-4400. Our team is highly qualified to put your mind at ease during your next visit.
Disclaimer: The information included in this article is for educational purposes only. It should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.

 (317) 745-4400
(317) 745-4400 info@danvilledentalcare.com
info@danvilledentalcare.com